
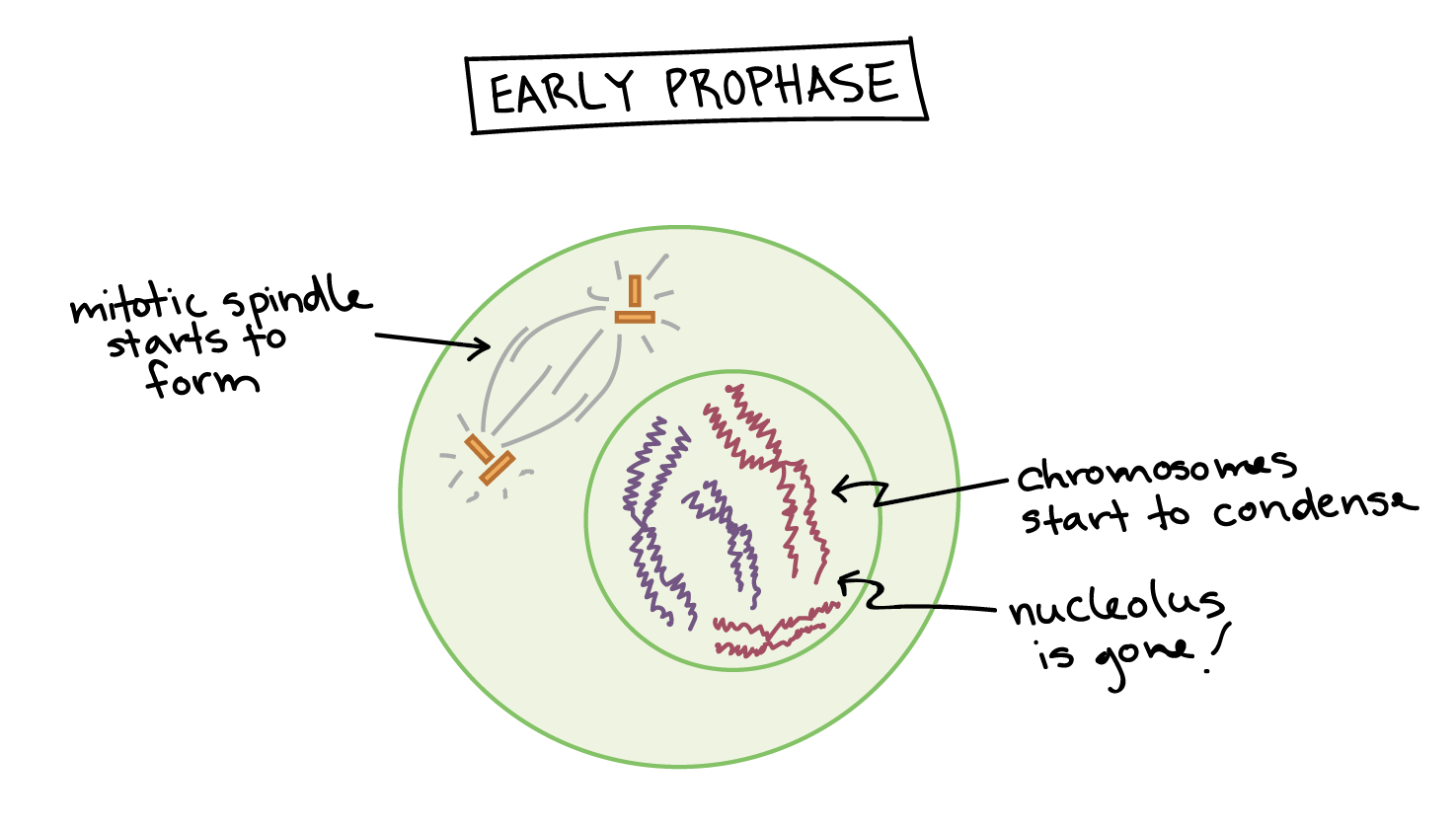
#PROPHASE DIAGRAM FREE#
Prophase generally involves number of phosphorylation which are induced by unavailability of free genetic material to express the suppressing role. In Metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs line up. Chromatin strands condense & coil, appearing as linear structures attached. Prophase is predominant by cellular preparation for the division includes the chromosomal condensation and disintegration of the cell organelles mainly nuclear membrane. This shuffling process is known as recombination or "crossing over" and occurs while the chromome pairs are lined up in Metaphase I. Replicated chromosomes are tightly coiled by chromosome condensation at the interphase. The miotic division is preceded by interphase, which is the phase where the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Each sibling is 50% mom and 50% dad, but which 50% of each can vary in the siblings. Mitotic division takes place in four major stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. But this happens independently for each trait, so just because you got your dad's brown eyes doesn't mean you'll get his blond hair too.

The sister chromatids remain attached to each other. Anaphase I The homologous chromosomes are pulled on the opposite poles. Each sperm and egg will end up with either B or b from mom and either B or b from dad. Prophase I is divided into five different stages: Leptotene Zygotene Pachytene Diplotene Diakinesis Metaphase I The homologous pairs of chromosomes are aligned on the equatorial plate. This leads to four possibilities: You could get B from mom and B from dad, or B from mom and b from dad, or b from mom and B from dad, or b from mom and b from dad. Imagine, for example, that eye color was controlled by a single gene, and that mom could have B, the allele for brown eyes or b, the allele for blue eyes, and dad could also have B or b. first phase of mitosis when chromatin condenses, nuclear envelope breaks down, the nucleolus. Van Benedin, while working on the horse threadworm (Parascarisequorum), observed in 1883 that there were. Homologous chromosomes form bivalents (or tetrads) and crossing. Haploid sex cells are produced from the diploid cells in meiosis. Most of the events that function to differentiate meiosis from mitosis occur in Prophase I. Label the diagram below with the following labels: Anaphase. It takes place in all sexually reproducing organisms.
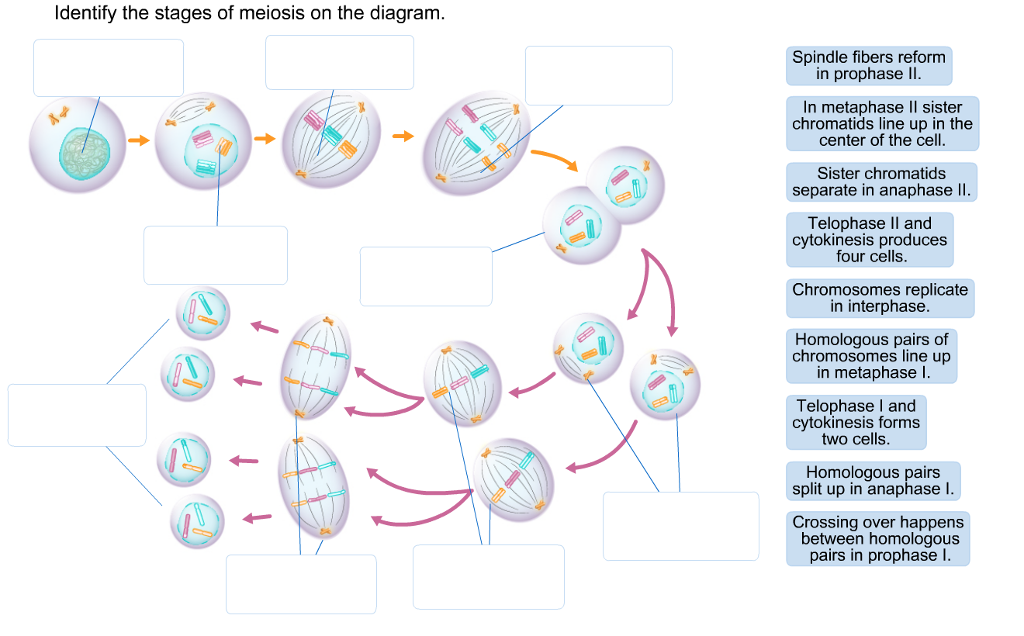
But each non-identical-twin child of these parents ends up with a different combination. The meiosis is a process of cell division by which the chromosomes are reduced from the diploid to the haploid number. You ended up with half of mom's paired genes and half of dad's paired genes. Your parents each have at least one pair of alleles (versions of a gene) for every trait (and many pairs of alleles for each polygenic trait).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
